Your Location:Home >Products >Biochemical Engineering >6893-26-1

Product Details
|
Chemical Properties |
White cryst. powder |
|
Uses |
D-Glutamic Acid is the unnatural (R)-enantiomer of Glutamic Acid, a non-essential amino acid. Its salt form (glutamate) is an important neurotransmitter that plays a key role in long-term potentiation and is important for learning and memory. D-glutamic acid is an optically active form of glutamic acid having D-configuration. It helps in the growth of Lactobacillus arabinosus. It can inhibit the IgE binding to peanut allergens. Glutamic Acid is also a key molecule in cellular metabolism. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: An optically active form of glutamic acid having D-configuration. |
|
General Description |
Glutamic acid is the most common excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. It is added to UDP-N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine (UDP-MurNAc-L-alanine) by the enzyme D-glutamic acid-adding enzyme (murD). This is, then, incorporated into the peptidoglycan precursor. Peptidoglycan makes up the cell walls of Gram-positive and -negative bacteria. The conversion of L-glutamate to D-glutamate by glutamate racemase (GR) enzyme is an essential step in the synthesis of peptidoglycan. |
|
Biological Activity |
Excitatory amino acid acting at NMDA receptors; less active than the L-isomer. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Unnatural isomer of glutamic acid. |
Isomeric SMILES: C(CC(=O)O)[C@H](C(=O)O)N
InChIKey: WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-GSVOUGTGSA-N
InChI: InChI=1S/C5H9NO4/c6-3(5(9)10)1-2-4(7)8/h3H,1-2,6H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)/t3-/m1/s1
Using cyclic voltammetry method, the anodic peak currents were found to have a linear relationship with the concentration of glutamic acids within the range between 0.5 and 15.0 mM, with a detection limit of 0.11 mM for L-glutamic acid and 0.26 mM for D-glutamic acid. The device-to-device reproducibility is great, confirming the robustness of this modification method.
The results suggested that Xanthine, 4-Pyridoxate, and d-glutamic acid may serve as potential biomarkers for pulmonary TB. The present study provides experimental basis for …
d-Amino acids are key intermediates requ...
Two biocatalytic reactions, transaminati...
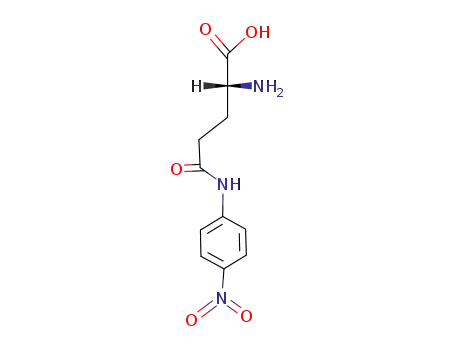
D-glutamic acid γ-p-nitroanilide

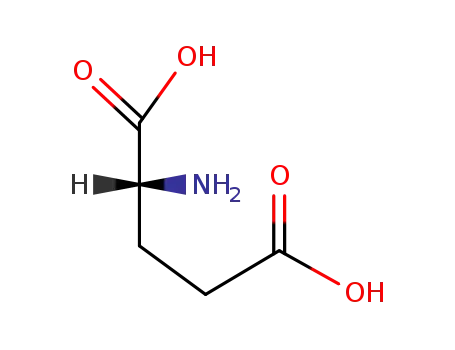
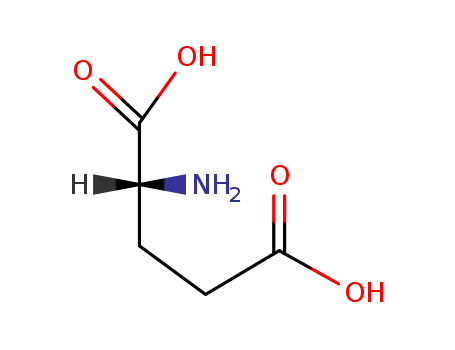
D-Glutamic acid
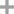
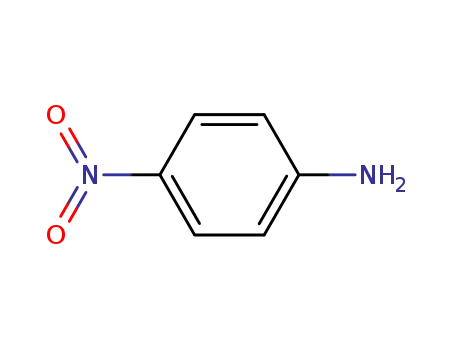
4-nitro-aniline
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With marine bivalve lysozyme; MOPS buffer; Tapes japonica; at 37 ℃; pH=7.0; Enzyme kinetics;
|
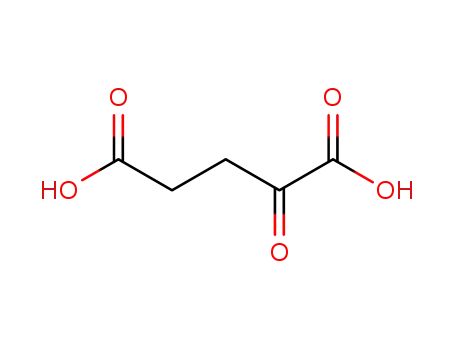
α-ketoglutaric acid

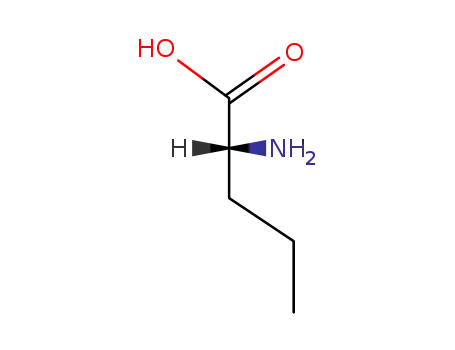
D-norvaline


D-Glutamic acid

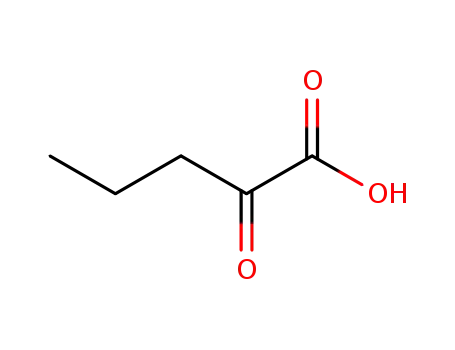
2-oxopentanoic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With pyridoxal 5'-phosphate; recombinant Lactobacillus salivarius UCC118 D-amino acid aminotransferase; In aq. phosphate buffer; at 30 ℃; for 0.0166667h; pH=7.5; Enzymatic reaction;
|
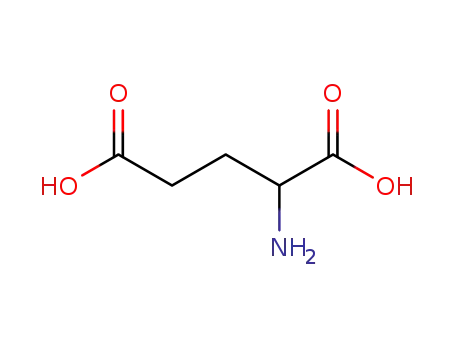
Glutamic acid
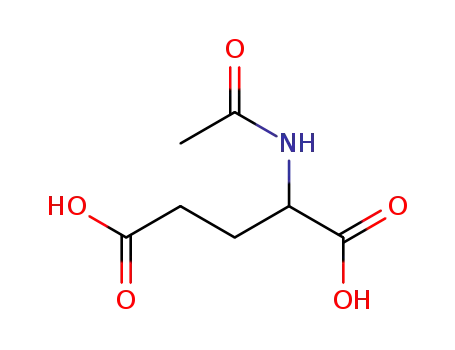
Acetyl-D,L-glutaminsaeure
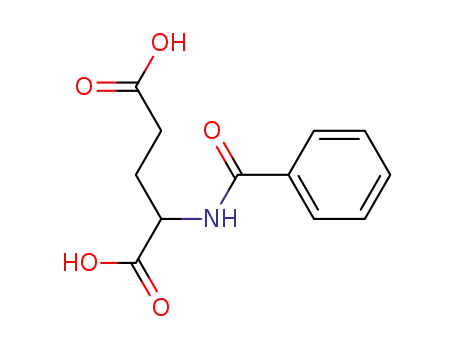
N-benzoylglutamic acid
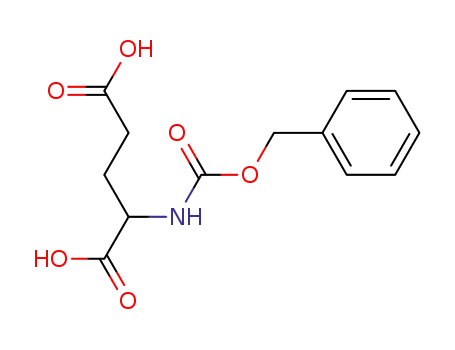
N-benzyloxycarbonyl-DL-glutamic acid
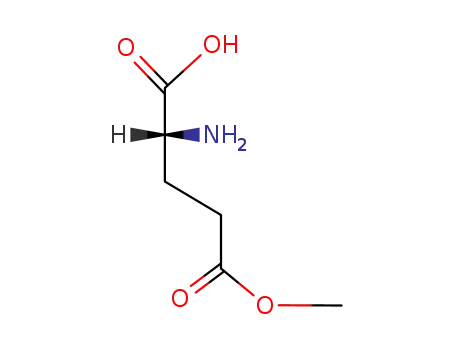
(R)-2-amino-5-methoxy-5-oxopentanoic acid
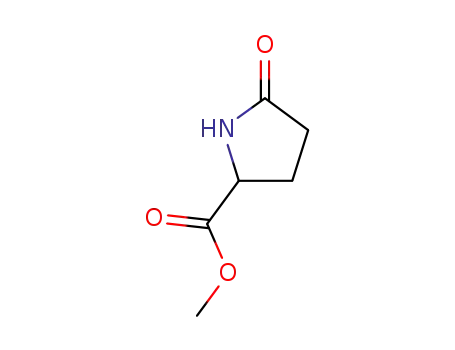
methyl 5-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxylate
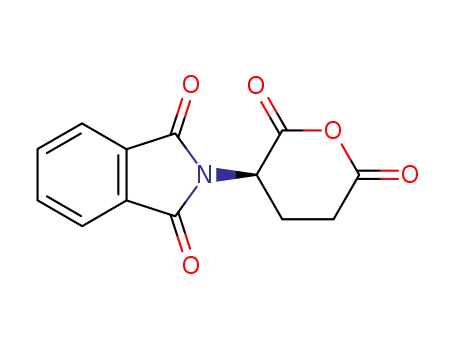
N-phthaloyl-D-glutamic acid anhydride
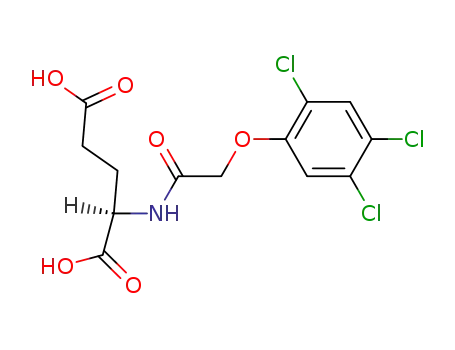
N-[(2,4,5-trichloro-phenoxy)-acetyl]-D-glutamic acid
CAS:56-12-2
CAS:7531-52-4
CAS:19764-30-8
CAS:4042-36-8