Your Location:Home >Products >Biochemical Engineering >56-12-2

Product Details
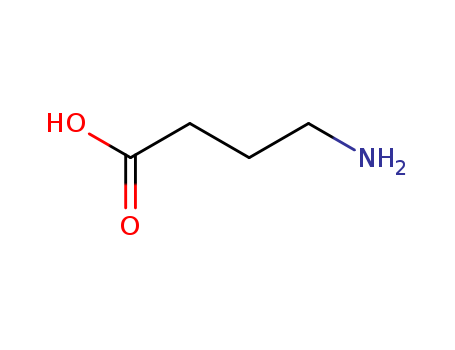
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a non-protein amino acid that accumulates in many plant species in response to environmental stress. The signaling role for γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) has been documented in animals for over seven decades. γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) plays a key role in regulating plant salinity stresstolerance. γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an amino acid not present in proteins. GABA participates in a variety of physiological functions and has received significant attention in the medical and food industries.
InChI:InChI=1/C4H9NO2/c5-3-1-2-4(6)7/h1-3,5H2,(H,6,7)
γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is a nonstructural amino acid that serves diverse functions in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Besides its widely established role in mammals as an inhibitory neurotransmitter, the diverse biological roles and metabolism of GABA in protozoan parasites have begun to be unveiled.
It is important to ensure food safety to study the technology and mechanism of pesticide residues degradation in crops. Though γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) has been widely reported to …
The oxidation of an amino acid, DL-ornit...
The kinetics of osmium(VIII) (Os(VIII)) ...
Background: Gamma aminobutyric acid (GAB...
The oxidation of DL-ornithine monohydroc...
γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) has several p...
We report a highly atom-efficient integr...
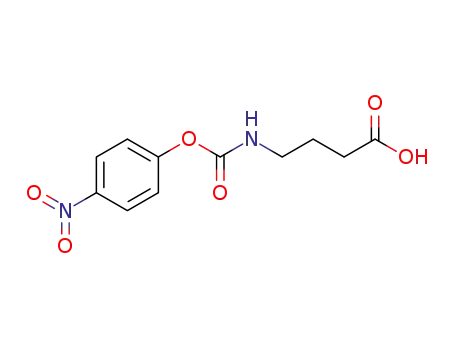
4-(p-nitrobenzyloxycarbonyl)aminobutanoic acid

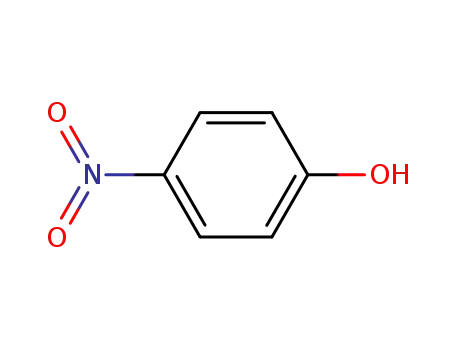
4-nitro-phenol
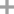
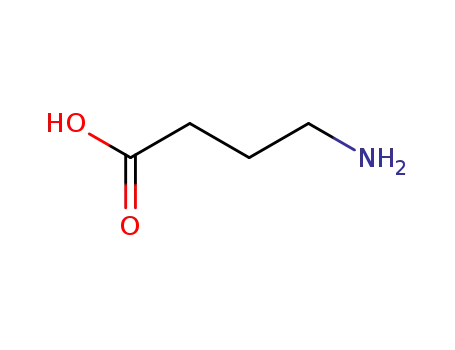
4-amino-n-butyric acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With water; antibody 33B4F11; at 25 ℃; Rate constant; pH = 7.0, NaCl;
|
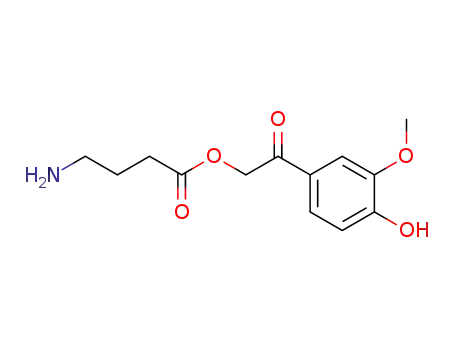
4-amino-butyric acid 2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenyl)-2-oxo-ethyl ester

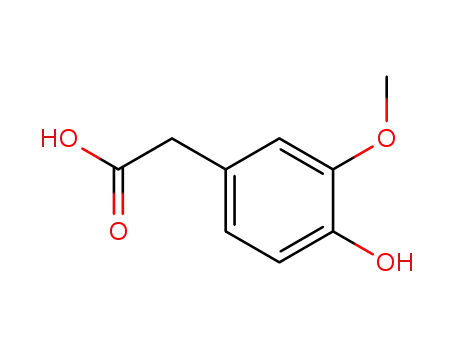
Homovanillic acid

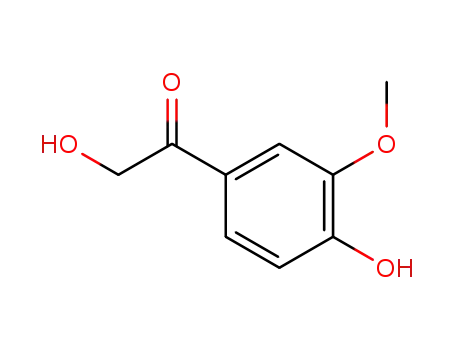
2,4'-dihydroxy-3'-methoxyacetophenone

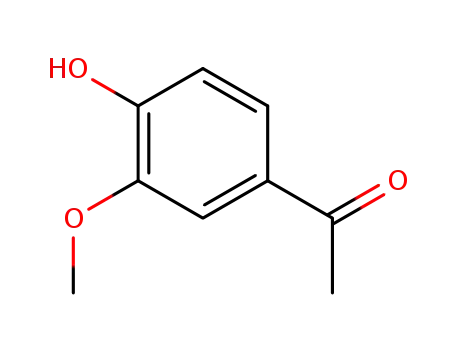
1-(3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanone


4-amino-n-butyric acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With water; UV-irradiation;
|
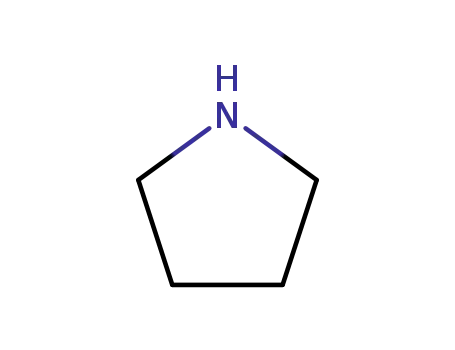
pyrrolidine
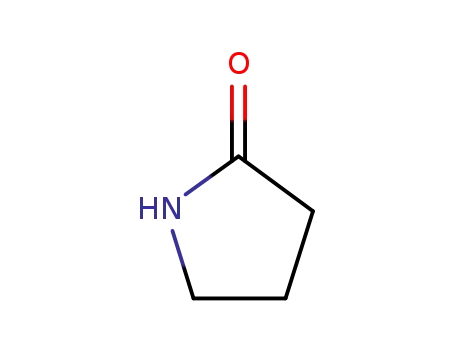
2-pyrrolidinon
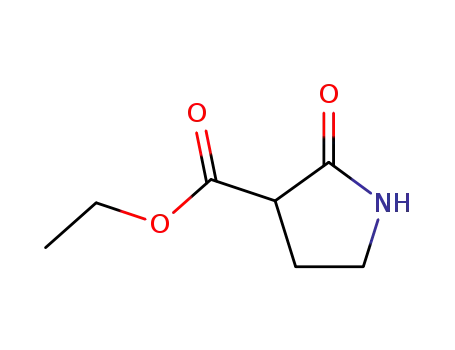
2-oxopyrrolidine-3-carboxylic acid ethyl ester
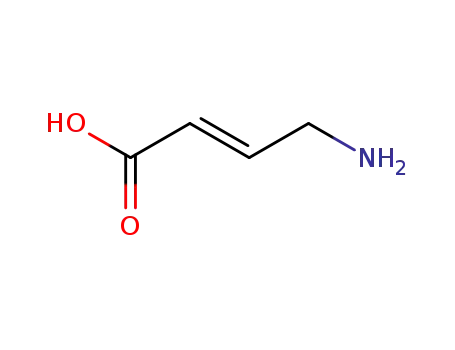
trans-4-aminocrotonic acid
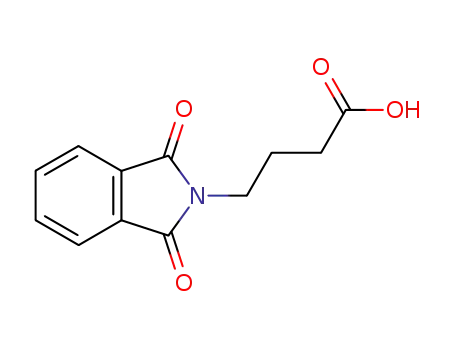
4-phthalimidobutyric acid
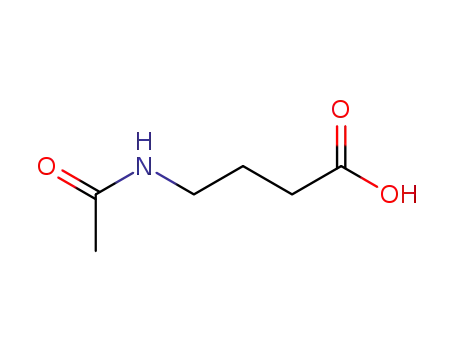
N-Acetyl-4-aminobutyric acid
4-(2,4-dinitro-anilino)-butyric acid
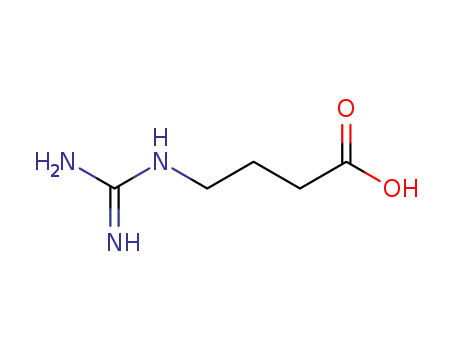
4-guanidinobutyric acid
CAS:7531-52-4
CAS:98-79-3
CAS:47375-34-8
CAS:84793-07-7