Your Location:Home >Products >Biochemical Engineering >673-06-3

Product Details
|
Description |
DL-Phenylalanine (DLPA) is an inhibitor of enzymes that inactivate enkephalins. D-Phenylalanine is distributed to the various tissues of the body via the systemic circulation. |
|
Chemical Properties |
White crystalline powder |
|
Uses |
Clinical studies suggest DPA may inhibit some types of chronic pain. D-Phenylalanine, the stereoisomer of L-Phenylalanine has been used in the synthesis of Schaeffer’s acid analogues as important structures in tuberculostatic design. They exhibit the ability to inhibit Mycobacterium tuberculosis type II dehydroquinase. D-phenylalanine has proven to be beneficial in many human patients with chronic, intractable pain. It is also anti-infiammatory. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Water soluble. Aqueous solutions are weakly acidic. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
D-alpha-Amino-beta-phenylpropionic acid may be light sensitive. D-alpha-Amino-beta-phenylpropionic acid reacts with strong oxidizing agents, acids and bases. . Act as weak acids in solution. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Flash point data for D-alpha-Amino-beta-phenylpropionic acid are not available, however D-alpha-Amino-beta-phenylpropionic acid is probably combustible. |
|
Safety Profile |
Mildly toxic by intraperitoneal route. Human systemic effects by ingestion: nausea, hypermotility, diarrhea. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. |
InChI:InChI=1/C9H11NO2/c10-8(9(11)12)6-7-4-2-1-3-5-7/h1-5,8H,6,10H2,(H,11,12)/t8-/m1/s1
Composite nanofiber (fP-NF) films were synthesized successfully by co-encapsulating E. coli O157 phages which isolated from domestic sewage and D-phenylalanine (D-Phe) into sodium alginate (SA)/polyethylene oxide (PEO) nanofibers by electrospinning.
In this work, D-phenylalanine (D-phe) was first introduced to improve the collectability and selectivity of sodium oleate (NaOL) for diaspore from kaolinite. The flotation performance of …
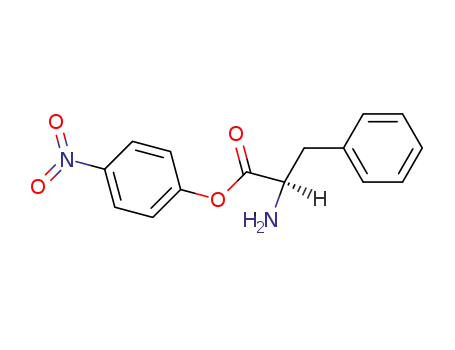
D-phenylalanine p-nitrophenyl ester

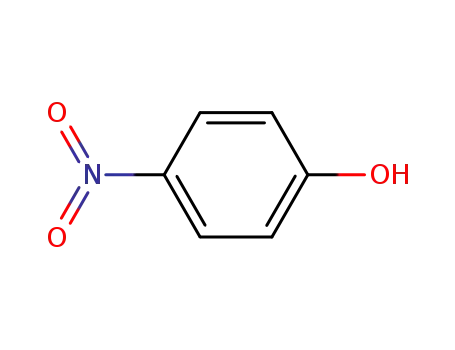
4-nitro-phenol
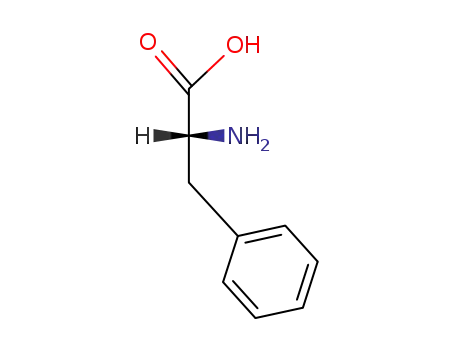
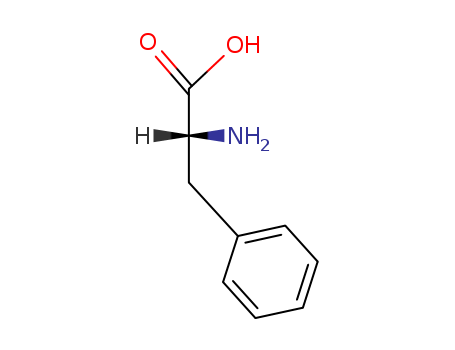
D-(R)-phenylalanine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With Enterobacter cloacae P99 β-lactamase; at 25 ℃; pH=7.5; Reagent/catalyst; Concentration; Kinetics; aq. buffer; Enzymatic reaction;
|
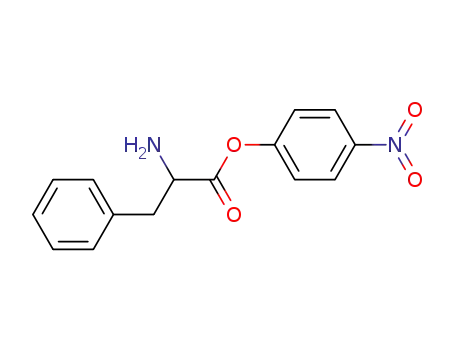
p-Nitrophenyl-D-phenylalaninate


4-nitro-phenol

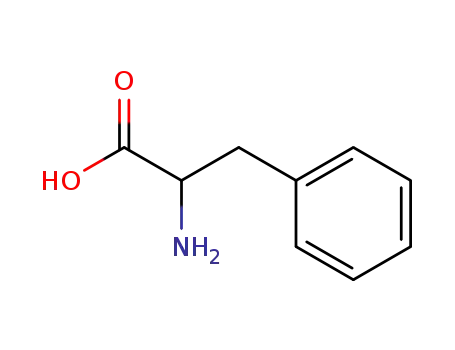
D-β-Phenyl-α-alanine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With Z-Phe-His-Leu; Tris-KCl buffer; water; cetyltrimethylammonim bromide; N,N-dimethyl-N-tetradecyltetradecan-1-aminium bromide; In acetonitrile; at 25 ℃; Rate constant; variation of ionic strength; enantioselectivity (L/D);
|
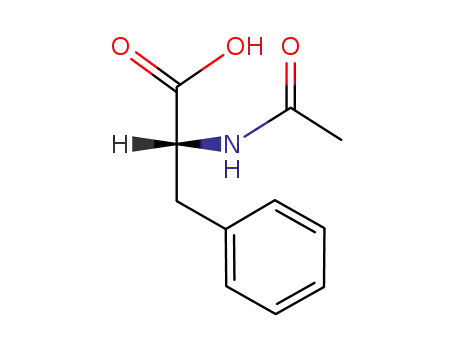
(R)-N-acetylphenylalanin
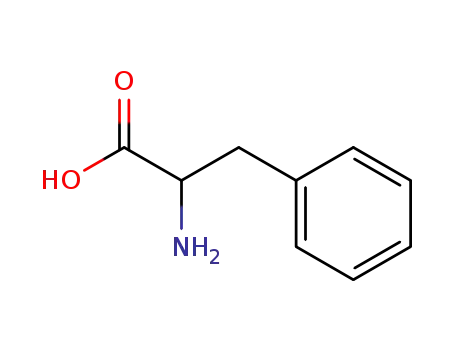
Phenylalanine
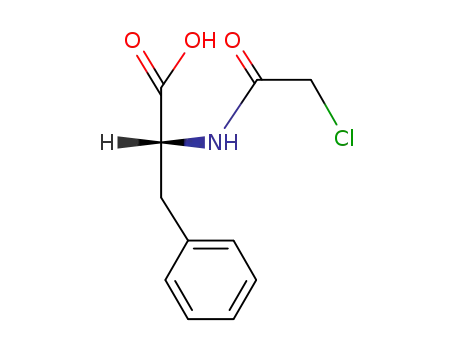
N-Chloroacetyl-D-phenylalanine
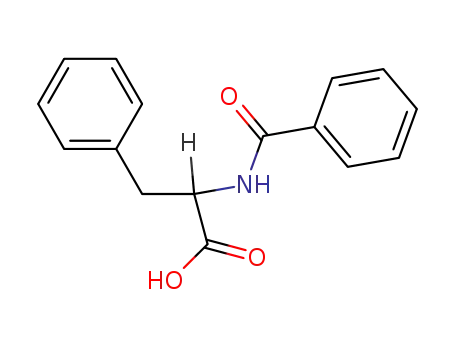
DL-N-benzoylphenylalanine
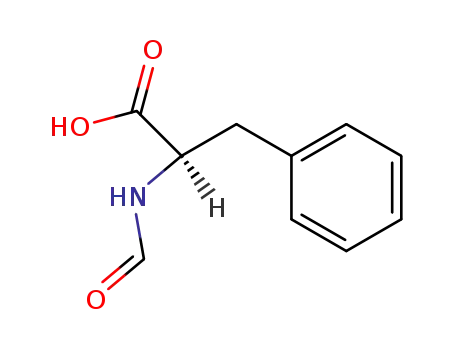
(-)-(R)-N-formylphenylalanine
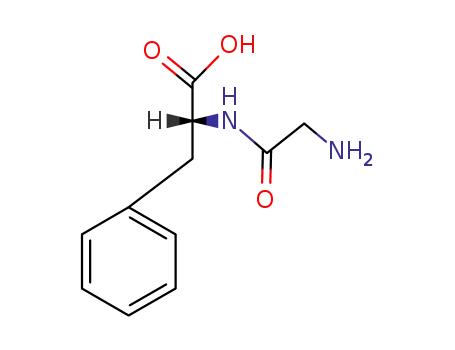
glycyl-D-phenylalanine
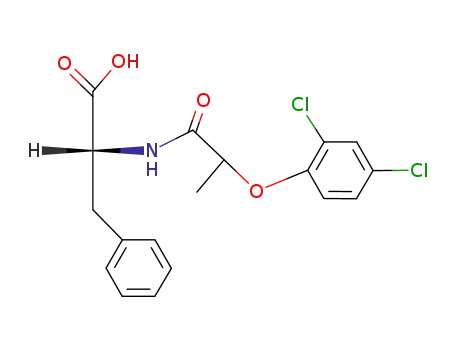
N-[(Ξ)-2-(2,4-dichloro-phenoxy)-propionyl]-D-phenylalanine
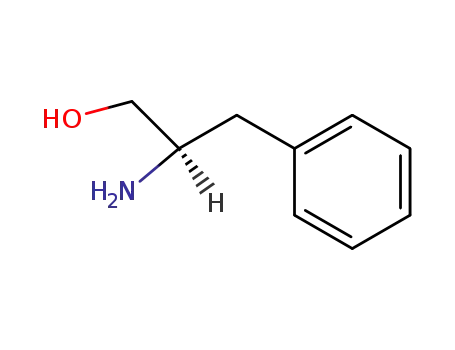
(R)-2-amino-3-phenylpropanol
CAS:56-12-2
CAS:7531-52-4
CAS:5959-95-5
CAS:338-69-2