Your Location:Home >Products >Biochemical Engineering >516-06-3
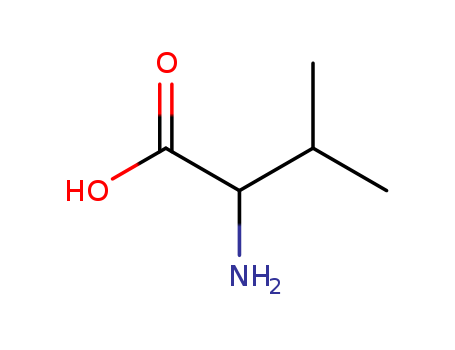

Product Details
|
Chemical Properties |
White crystalline powder |
|
Occurrence |
Reported found in many fruits, plants and animal tissues; in milk and dairy products. |
|
Preparation |
By the action of ammonia on α-bromoisovaleric acid; also through a hydantoin intermediate. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: A branched-chain amino acid that consists of glycine in which one of the hydrogens attached to the alpha-carbon is substituted by an isopropyl group. |
| Use | DL-Valine promotes muscle growth and tissue repair. L-valine helps build muscle by bringing more glucose to the muscles as they are stressed and worked. |
InChI:InChI=1/C5H11NO2/c1-3(2)4(6)5(7)8/h3-4H,6H2,1-2H3,(H,7,8)
Poly (DL-valine) modified multiwalled carbon nanotube paste sensor (PVLMCNTPS) was prepared by electro-polymerization route.
The reaction of DL-valine hydroxamic acid with triacetonamine proceeds as the N,N'-regioselective condensation to form (±)-1-hydroxy-3-isopropyl-7,7,9,9-tetramethyl-1,4,8-triazaspiro[4,5]decan-2-one.
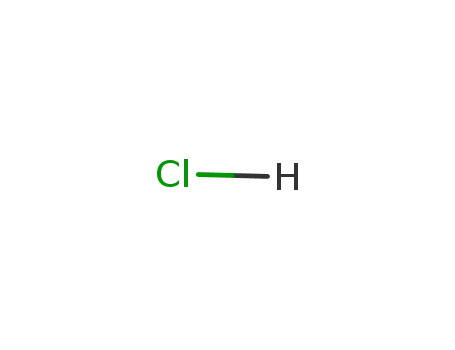
hydrogenchloride
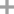
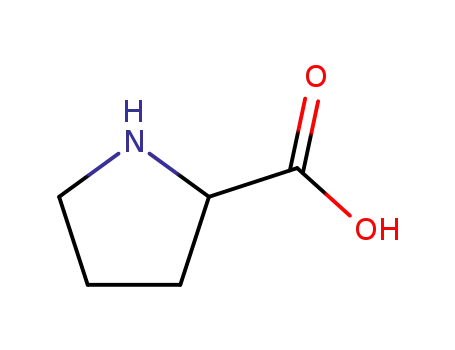
rac-Pro-OH

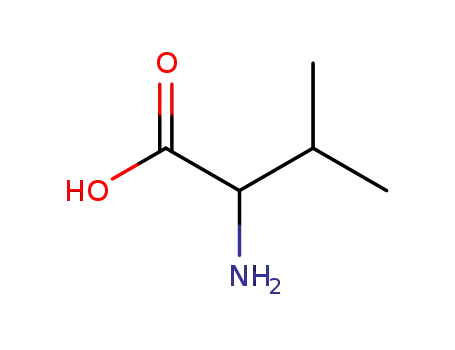
D,L-valine

?Tyr

LEUCINE

Trp
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
UV-Licht.Irradiation;
|
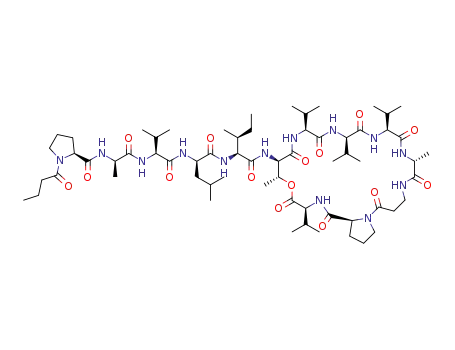
xenoamicin A

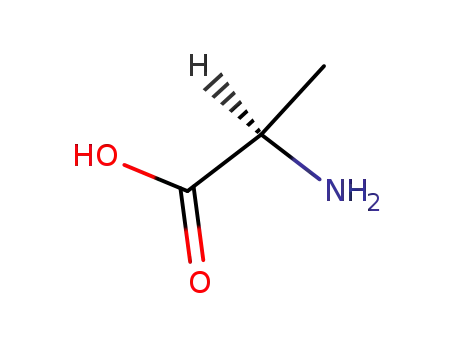
D-Alanine

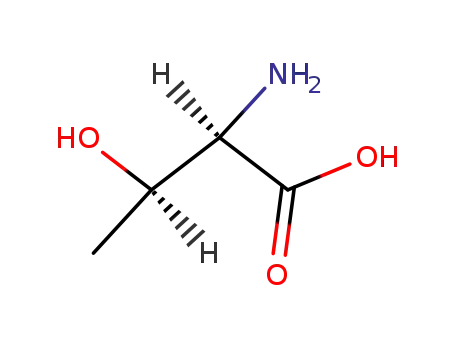
D-allo-threonine

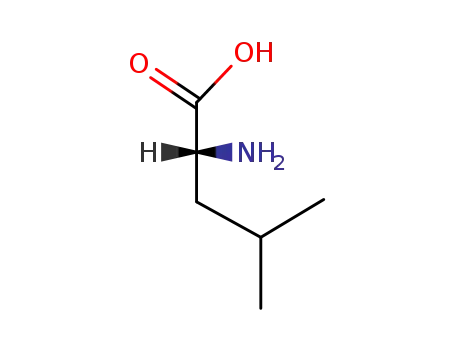
(R)-leucine

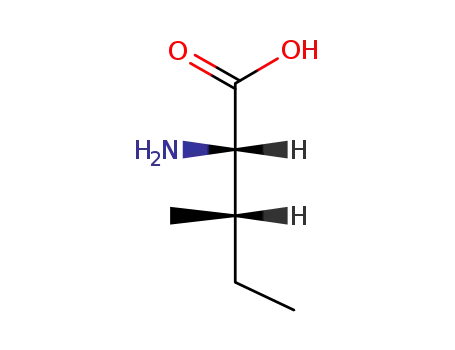
L-isoleucine


D,L-valine

L-proline
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hydrogenchloride; water; at 110 ℃; for 16h; High pressure;
|
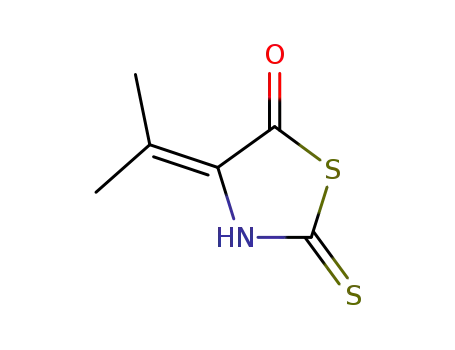
4-isopropylidene-2-thioxo-thiazolidin-5-one
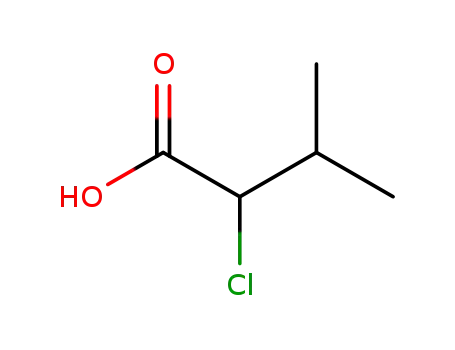
2-chloro-3-methylbutanoic acid
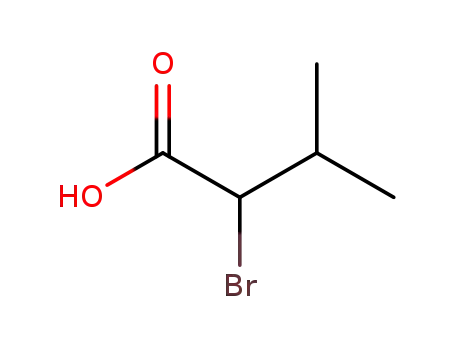
2-bromoisovaleric acid
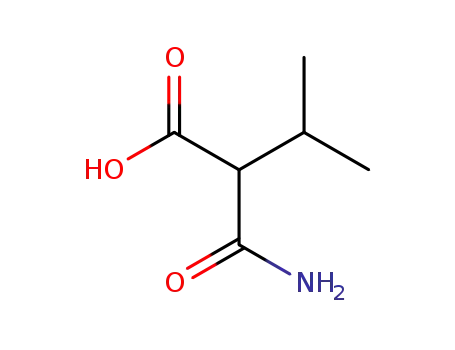
2-isopropyl-malonamic acid
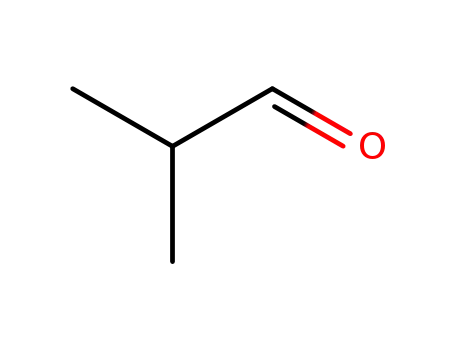
isobutyraldehyde
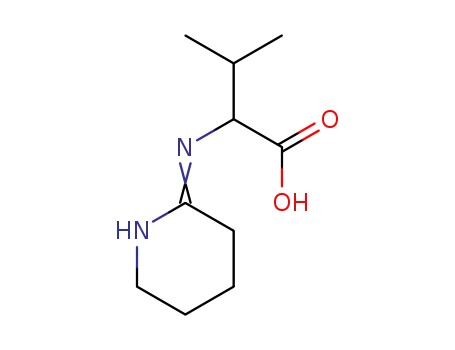
N-[2]piperidylidene-valine
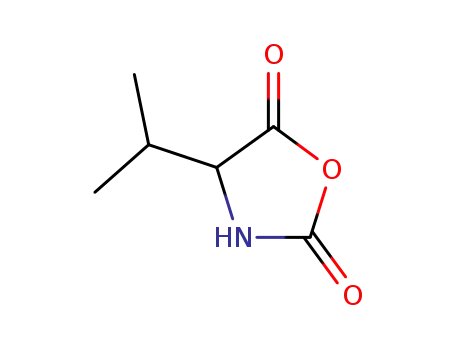
4-isopropyl-2,5-oxazolidinedione
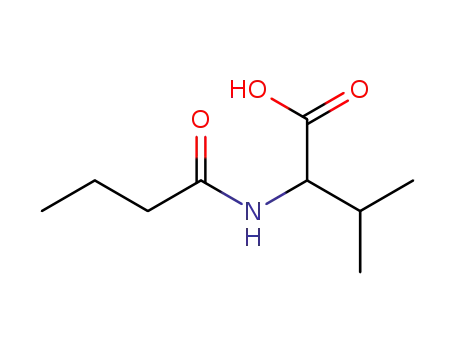
N-butyrylvaline
CAS:56-12-2
CAS:7531-52-4
CAS:617-65-2
CAS:59-51-8